PM Narendra Modi Hails ISRO’s Extraordinary Feat
In a historic achievement, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully placed Aditya-L1, India’s first space-based solar observatory, into its designated orbit, Lagrange Point-1. The momentous announcement was made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who lauded the relentless dedication of Indian scientists in realizing one of the most complex space missions to date.
Lagrange Point-1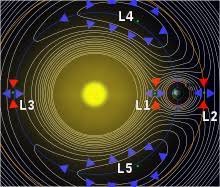
The Lagrange Point-1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, situated approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, serves as the ideal location for solar observations. This unique point allows a satellite in a halo orbit around L1 to continuously observe the Sun without encountering occultations or eclipses. The uninterrupted view from this vantage point provides a substantial advantage in studying solar activities and their impact on space weather in real-time.
Journey of Aditya-L1: A Technological Triumph
The journey of Aditya-L1 commenced on September 2, 2023, with a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C57) launching the spacecraft from the second launch pad of the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota. After a 63-minute flight, Aditya-L1 was successfully injected into an elliptical orbit around Earth. Subsequent maneuvers allowed the spacecraft to escape Earth’s sphere of influence and head towards the Sun-Earth L1 point.
Seven Payloads for Comprehensive Solar Observations
Aditya-L1 is equipped with seven payloads designed to observe the Sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, and outermost layers, known as the corona. These observations are facilitated through a combination of electromagnetic and particle detectors, as well as magnetic field detectors. Four of the payloads have the unique capability to directly view the Sun, providing detailed insights into its various layers and phenomena.
In-situ Studies at Lagrange Point-1
Three payloads on Aditya-L1 focus on in-situ studies of particles and fields at Lagrange Point-1. This aspect of the mission contributes to essential scientific research on the propagatory effects of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium. The spacecraft’s unique position at L1 allows for detailed studies that would be challenging from other locations.
Prime Minister Modi’s Acknowledgment
 Prime Minister Modi expressed confidence in India’s commitment to pursuing new frontiers of science for the benefit of humanity. His acknowledgment of the relentless dedication of Indian scientists reflects the national pride associated with such accomplishments. The successful placement of Aditya-L1 into its designated orbit marks a significant milestone for India’s space exploration endeavors.
Prime Minister Modi expressed confidence in India’s commitment to pursuing new frontiers of science for the benefit of humanity. His acknowledgment of the relentless dedication of Indian scientists reflects the national pride associated with such accomplishments. The successful placement of Aditya-L1 into its designated orbit marks a significant milestone for India’s space exploration endeavors.
Technological Challenges and ISRO’s Expertise
The Lagrange Point-1, being approximately one percent of the total distance between the Earth and the Sun, poses challenges that require advanced technological solutions. ISRO’s ability to navigate these challenges and position Aditya-L1 precisely in this specialized orbit highlights the organization’s expertise and innovation in the field of space exploration.
Aditya-L1’s Mission and Potential Contributions
As Aditya-L1 embarks on its mission to study the Sun’s various layers and activities, it holds the potential to contribute significantly to our understanding of solar dynamics and their implications for space weather. The continuous observations from the vantage point of Lagrange Point-1 will provide researchers with a wealth of data, allowing for more accurate predictions and analyses of solar phenomena.
Reinforcing India’s Global Standing
The successful execution of the Aditya-L1 mission reinforces India’s position as a formidable player in the global space exploration landscape. The country’s space program has consistently demonstrated its capabilities, with milestones including successful satellite launches, lunar missions, and Mars orbiter missions in recent years.
India’s Growing Prowess in Space Exploration
In conclusion, the successful placement of Aditya-L1 in its designated orbit is a testament to India’s growing prowess in space exploration. This mission not only adds to the nation’s list of achievements but also contributes valuable data to the global scientific community’s understanding of the Sun and its dynamics. As Aditya-L1 continues its observations from Lagrange Point-1, it is poised to make significant contributions to solar science, space weather studies, and humanity’s quest for knowledge beyond Earth’s boundaries.











Comments 1