India’s foreign exchange reserves are a critical indicator of the country’s economic stability and resilience in the global financial landscape. As of February 16, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reported a decline in India’s forex reserves to $616.10 billion, reflecting a decrease of $1.13 billion from the previous week.
This decline follows a more significant drop of $5.24 billion recorded in the week ending February 9, marking the lowest reserve level in two months since December 15.
Decline in Foreign Exchange Reserves
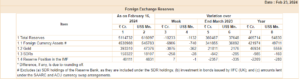 The recent decline in India’s foreign exchange reserves warrants attention, signalling potential shifts in the country’s economic landscape.
The recent decline in India’s foreign exchange reserves warrants attention, signalling potential shifts in the country’s economic landscape.
At $616.10 billion, the reserves have decreased by $1.13 billion compared to the previous week, indicating ongoing fluctuations in global financial markets.
This decline follows a larger drop observed in the week ending February 9, which highlights the vulnerability of reserve levels to external economic factors. Understanding the reasons behind these fluctuations is crucial for assessing India’s economic health and its capacity to navigate global uncertainties.
Composition of Reserves
Breaking down the composition of India’s foreign exchange reserves provides insights into the country’s asset allocation and diversification strategy. As of February 16, foreign currency assets accounted for the majority of the reserves, totalling $545.78 billion.
 Gold reserves amounted to $47.38 billion, while Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) stood at $18.11 billion. Additionally, the reserve position in the International Monetary Fund (IMF) was reported at $4.83 billion.
Gold reserves amounted to $47.38 billion, while Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) stood at $18.11 billion. Additionally, the reserve position in the International Monetary Fund (IMF) was reported at $4.83 billion.
This breakdown outlines India’s efforts to maintain a balanced reserve portfolio, mitigating risks associated with currency fluctuations and market volatility.
Factors Influencing Reserve Changes
Several factors contribute to changes in India’s foreign exchange reserves, reflecting the dynamic nature of global financial markets. Transactions involving the sale or purchase of foreign assets, as well as fluctuations in currency valuations, play a significant role in shaping reserve levels.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) closely monitors these factors, intervening in the market when necessary to stabilize the rupee’s exchange rate and safeguard the country’s economic interests. Despite the recent decline in reserves, the RBI’s proactive approach aims to maintain stability and confidence in India’s currency market.
Future Outlook and Expectations
Looking ahead, there are reasons for cautious optimism regarding India’s foreign exchange reserves and their trajectory. The inclusion of Indian government bonds in JPMorgan’s global indices, scheduled to begin in June, is expected to attract substantial foreign investment.
Economists anticipate inflows of more than $20 billion into Indian sovereign debt over a ten-month period, potentially bolstering reserve levels. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) aims to manage these inflows strategically, ensuring that they contribute to long-term economic stability while preventing sharp appreciation of the rupee.
Overall, the future outlook for India’s foreign exchange reserves hinges on effective reserve management and proactive measures to navigate evolving global economic dynamics.
India’s foreign exchange reserves stand as a bulwark against economic volatility, serving as a cornerstone of the country’s financial stability. While recent declines in reserves have raised eyebrows, they also highlight the need for vigilant monitoring and strategic management.
As the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) navigates these fluctuations, it must employ a multifaceted approach that combines prudent risk management with proactive policy interventions.
 Diversification remains key to supporting resilience against market shocks. By maintaining a balanced portfolio of foreign currency assets, gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), and IMF positions, India can mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations and market turbulence.
Diversification remains key to supporting resilience against market shocks. By maintaining a balanced portfolio of foreign currency assets, gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), and IMF positions, India can mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations and market turbulence.
This approach not only shields the economy from external shocks but also fosters investor confidence and strengthens India’s position as a robust financial hub.
However, challenges persist on the horizon. The RBI must remain vigilant against external headwinds, such as geopolitical tensions and global economic uncertainties, which could impact reserve levels and currency stability.
Moreover, the central bank must strike a delicate balance between managing inflows to prevent excessive rupee appreciation and fostering a conducive environment for foreign investment.
India’s foreign exchange reserves are not merely a numerical metric but a symbol of the country’s economic strength and resilience. By adopting a proactive and forward-thinking approach to reserve management, India can navigate the complexities of the global financial landscape and emerge stronger in the face of adversity.
As the RBI continues to chart its course, the overarching goal remains unchanged to safeguard India’s economic stability and prosperity for generations to come.











Comments 1